Tritone
Glossary
A tritone is the interval between one note and a note three whole tones higher (or lower, also six semitones), with a ratio of √2:1,  dividing the octave perfectly in half.
dividing the octave perfectly in half.

The tritone plays an important role in dominant seventh chords, since its dissonance pleasantly resolves to the perfect fourth or the perfect fifth.
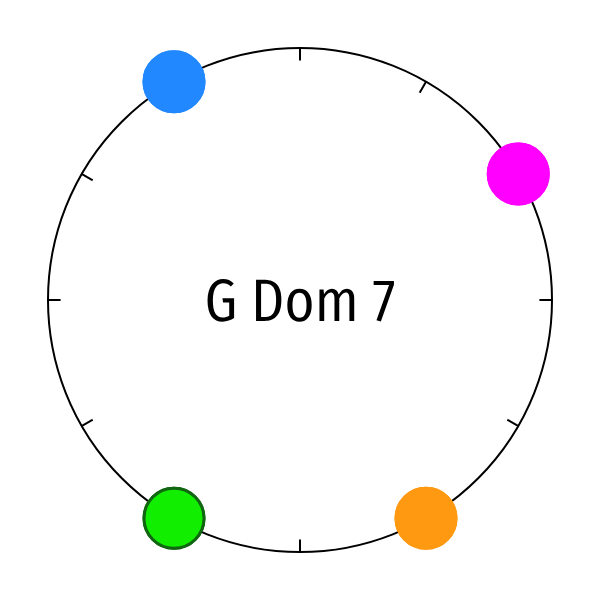
This example  shows the tritone of G Dom 7 (B and F) resolving to the C and E of a C Major chord.
shows the tritone of G Dom 7 (B and F) resolving to the C and E of a C Major chord.
For set classes with tritones, see Tritonic. For set classes without tritones, see Atritonic.
See Pitch & Intervals for the basics on where the tritone comes from, and see intervals for various intervals of the same size with different names.
A tritone is the interval between one note and a note three whole tones higher (or lower, also six semitones), with a ratio of √2:1, dividing the octave perfectly in half.
The tritone plays an important role in dominant seventh chords, since its dissonance pleasantly resolves to the perfect fourth or the perfect fifth.

This example shows the tritone of G Dom 7 (B and F) resolving to the C and E of a C Major chord.
For set classes with tritones, see Tritonic. For set classes without tritones, see Atritonic.
See Pitch & Intervals for the basics on where the tritone comes from, and see intervals for various intervals of the same size with different names.